Domains from the literature
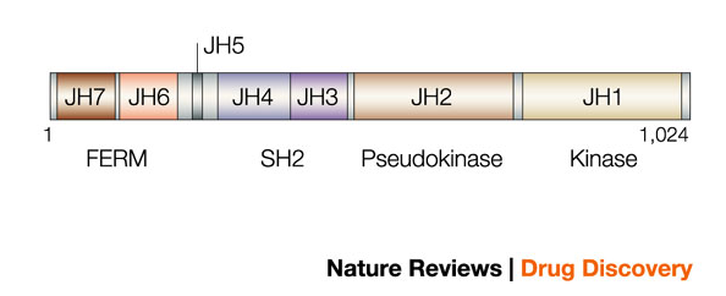
The homology domains (JH1 - JH7) are numbered starting from the carboxy terminal end of the protein and correlate to four functional domains. JH1 (the kinase domain) and the JH2 domain (the psudokinase domain) are the two domains which work together and inspired the naming of the Janus Kinase family of proteins after the Roman god Janus who was supposed to have two faces on opposite sides of his head. The pseudokinase domain is where the STAT molecules interact in the JAK/STAT pathway. The JH3 and JH4 homology domains are part of the SH2 domain which recognizes phosphorylated tyrosine. The JH5 homology domain is not a part of one of the four functional domains and its role is not well documented. JH6 and JH7 are part of the FERM or four-point-one ezrin/radixin/moesin domain which binds the JAK3 protein to the common gamma subunit of cytokine receptors. [1][2]
Domains found using SMART
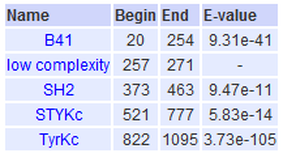
Figure 3: Table of domains identified by SMART [3]
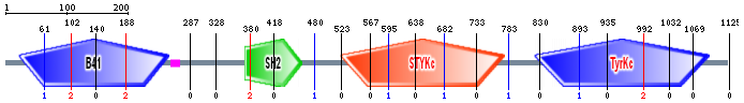
Inputting the protein sequence into the SMART database returned the diagram in Figure 2 showing four domains. The B41, SH2, STYKc and TyrKc domains are present in Figure 2 with their locations indicated in Figure 3. The "low complexity" domain listed in the table is indicated in figure 2 by the small pink box to the right of B41. Two other low complexity domains were also identified by SMART, one from position 208 to 226 and one from 1050 to 1056. These domains were also considered not significant enough to include in Figure 2 and because they overlap with the B41 and TyrKc domain, they were not included in Figure 3. Those two low complexity domains were not identified in the literature.
These results can be compared to the domains indicated in the literature. The TyrKc domain is the kinase domain from figure 1, the STYKc domain is the pseudokinase domain. The SH2 domain is labled in both figures 1 and 2, and the B41 domain from figure 2 is the FERM domain from figure 1. The JH5 homology domain in figure 1 is most likely the low complexity domain represented by the pink box in figure 2.
Domains found using Pfam
Pfam (see figure 4) was able to identify two Pkinase_Tyr domains and one SH2 domain (not shown). The first Pkinase_Tyr domain (shown on the left above) is located from position 521 to 777 and correlates to the pseudokinase and STYKc domains of figures 1 and 2 respectively. The second Pkinase_Tyr domain (shown on the right above) is located from position 823 to 1093 and correlates to the Kinase and TyrKc domains of figures 1 and 2. The SH2 domain is located from position 377 to 454. Pfam did not find the FERM/B41 domain or the JH5 homology domain/low complexity region.
References
[1] O'Shea, J.J., Pesu, M., Borie, D.C., Changelian, P.S. (2004) A new modality for immunosuppression: targeting the JAK/STAT pathway, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 3:555-564. doi: 10.1038/nrd1441
[2] Notarangelo, L.D., Mella, P., Jones, A., de Saint Basile, G., Savoldi, G., Cranston, T., Vihinen, M., Schumacher, R.F. (2001). Mutations in severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) due to JAK3 deficiency. Human Mutation, 18(4):255-63. doi: 10.1002/humu.1188
[3] http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/
[4] http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/